<Introduction>
✪Fatty acid are long chain carboxylic acids.
✪Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds.
Palmitic acid(palmitate) is the primary end product of fatty acid synthesis.
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2Ch2CH2CH2Ch2CH2CH2CH2CH2COO-
àPalmitate C16:0
✪Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds.有雙鍵的稱為不飽和脂肪酸
Human can synthesize only a few of the unsaturated fatty acids,
the rest come rom essential fatty acids in the diet
that are transported as triglycerides from the intestine in chylomicrons.
人類因為酵素關係無法合成一些不飽和脂肪酸,因此必須注意必須不飽和脂肪酸的攝取。
✪Two important essential fatty acids are linolenic acid and linoleic acid.
àimportant in membrane phospholipid to maintain normal fluidity
of cell membranes essential for many functions.
1. Linoleic C18:2(9:12)在C9-10 and C12-13之間有雙鍵=ω-6 family(18-12=6)
2. Linolenic C18:3(9,12,15)= ω-3 family
3. Arachidonic C20:4(5,8,11,14)= ω-6 family
✪Double bonds in fatty acids are in cis-configuration.通常雙鍵脂肪酸以順式為表現
Trans- double bonds are unnatural and predominate in fatty acids
found in margarine(植物奶油) and other foods where
partial hydrogenation of vegetable oils is used in their preparation.

比較起來液態的油,這些局部氫化過的脂肪酸在較冷的溫度下較容易固態化。
少吃啊!!!
When incorporated into phospholipids that constitute membranes,
trans-fatty acids decreased membrane fluidityà
Trans-fatty acids and saturated fatty acids are associated with increase risk of atherosclerosis.
反式脂肪酸和飽和脂肪酸被認為為心血管粥狀動脈硬化的危險因子。
Clinical correlate:
Cardioprtective effects of Omega-3 Fatty acids(鮭魚, 鮪魚, and herring(鯡魚)
and in some nuts(walnuts 核桃類 ) and seeds(flax seed亞麻子))

機轉àreplace some of the arachidonic aicd in platelet membranes and may
lower the production of thromboxane and the tendency of the platelets to aggregate.
Diet high in omega-3 fatty acids has also been associated with a decrease in serum triglycerides.
多吃!!!
Activation of Fatty acids:
Fatty acid +CoA +ATPàFatty acyl CoA+ AMP+PPi
當脂肪酸要用於代謝時,通常都要先轉為活化態fatty acyl CoA.
<脂質的吸收>
成人每日約攝食60-150g脂質,其中90%以上常為Triglyceride
多餘的飲食脂質被用來製造膽固醇,膽固醇酯,磷脂質即未脂化的脂肪酸。
在胃中:
脂質消化在胃中開始,由acid-stable lipase所催化(被認為源自舌背的腺體lingual lipase)
TG分子中尤其含有短或中脂肪酸鏈長度(少於12C 牛奶的脂質)是此酶主要的作用物,
相同的三醯甘油也可經胃黏膜分泌的gastric lipase降解。
這兩種酶為酸穩定的(PH4-6),在嬰兒的脂質消化尤為重要,因為牛奶的脂質是熱量的主要來源。
在胰臟有缺失的成人如cystic fibrosis,此酵素也很重要。
這兩個酶在pancreatic lipase缺失下可以幫助這些病人降解TG。尤其是短或中脂肪酸鏈長度。
在小腸中的乳化作用:
脂質乳化的關鍵在十二指腸。
1. bile salts作用(由肝臟合成儲存在膽囊)2. 蠕動的機械性混合作用
Pancreatic enzyme:
1. TG:
esterase 分解後留下2-monoacylglycerol and free fatty acids
( 此酶在胰臟酶的分泌中有很高的濃度約占2-3% protein ).
Colipase:由胰臟分泌,與lipase 1:1結合,鑲嵌在脂質與水的交界面。
以prolipase形態分泌,在腸道經trypsin活化。
àOrlistat 為一種減肥藥,抑制胃與胰脂解酶,減少脂質吸收,達到減重的目的。
2. Cholesterol ester:
飲食中的膽固醇大部分是以游離態(非酯化)存在。
有10-15%是以酯化的形態。
由cholesterol ester hydrolase(cholesterol esterase)水解,
其產物為膽固醇與游離FA。膽鹽存在時,此酶活性顯著增加。
3. Proenzyme:
phopspholipase A2, 可被trypsin 活化,膽鹽可使活性增加,
可移除磷脂質的二號碳上的FAàlysophospholipid.
可再由lysophopholipaseàglycerylphosphoryl base.排泄于糞便或進一步降解吸收。
脂質消化的激素控制:
在空腸與下十二指腸的黏膜細胞à
CCK:在脂質與部分消化的蛋白質進入小腸時激素會作用在膽囊使膽囊收縮與使膽汁釋出。
胰臟的外泌細胞上使胰臟酵素分泌。也可降低胃的蠕動使進入小腸速度放慢。
Secretin: 使胰臟和肝臟釋出富含Bicarbonate的水性溶液,可幫忙中和腸內容物的PH質。

統整:
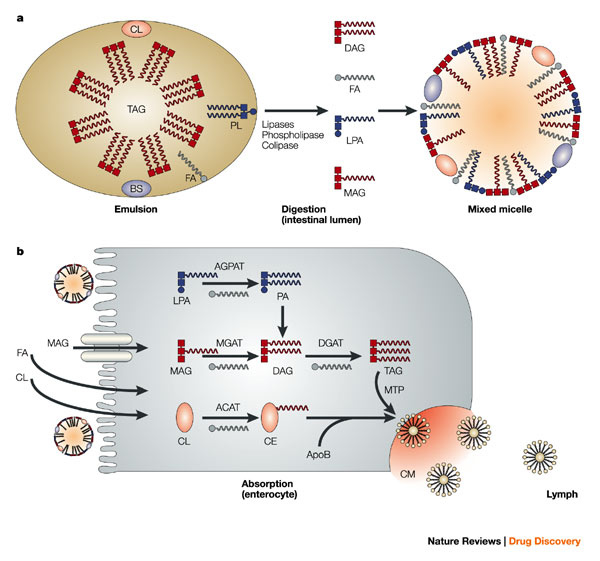
Typical high fat meal contain gram level amount of TG and milligram-level of cholesterol and cholesterol esters.
On entry into the intestinal lumen, bile is secreted by the liver to emulsify the lipid contents.
The pancreas secretes pancreatic lipase, colipase, cholesterol esterase
and degrade the lipids to 2-monoglyceride, fatty acids, and cholesterol.
These lipids are absorbed and re-esterified to TG and cholesterol esters and packaged, along with Apoprotein B-48
and other lipids(fat-soluble vitamins), into chylomicrons.
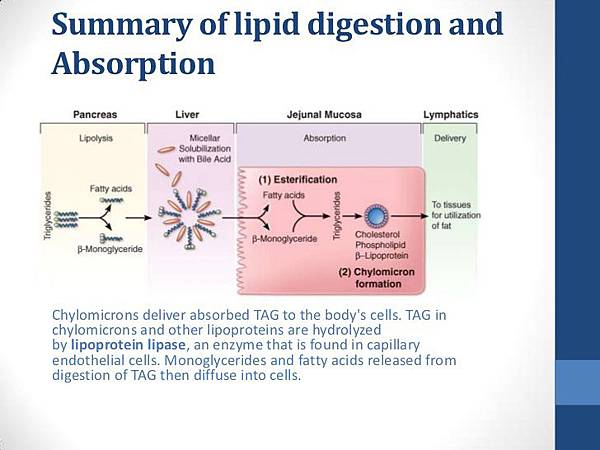
Normally there is very little lipids loss in the stool.
Defects in lipid digestion result in steatorrhea, where there is an excessive amount of lipids in the stool(fatty stools.)
<Fatty acid biosynthesis>脂肪酸的合成
主要在Liver, lactating mammary gland 合成fatty acid
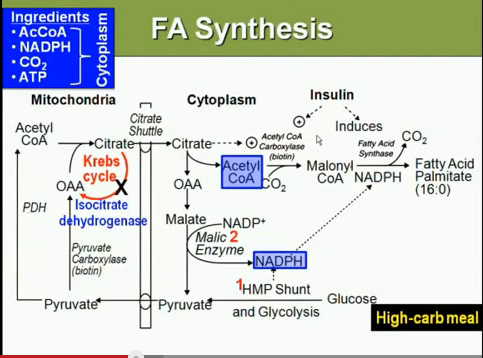

Excess dietary glucose can be converted to fatty acids in the liver and sent to the adipose tissue for storage.
Adipose tissue synthesize smaller quantities of fatty acids.
脂肪酸主要被製造成TG而儲存於脂肪細胞中。
Insulin promotes many steps in the conversion of glucose to acetyl-CoA in the liver:
胰島素被視為促進製造脂肪酸和TG的酵素。
1. Glucokinase(induced)
2. PFK-2/PFK1(PFK-2 dephosphorylated)
3. Pyruvate dehydrogenase(dephosphorylated)
Both of the major enzymes of fatty acid synthesis are also affected by insulin:
1. Acetyl CoA carboxylase(dephosphorylated, activated)
2. Fatty acid synthase(induced)
Citrate Shuttle and Malic enzyme:在合成脂肪酸中重要的酵素和機轉
Citrate shuttle transports acetyl-CoA group from the mitochontria to the cytoplasm for fatty acid synthsis.
In mitochondria:
Acetyl-CoA+OAAàcitrateàtransported into the cytoplasm.
(indirectly promote this process include insulin and high energy status)
In the cytoplasm: citrate lyase splits citrate back into acetyl –CoA and OAA.
The OAA returns to the mitochondria to transport additional acetyl-CoA.
此反應包含重要的malic enzyme,使細胞質中除了HMP shunt 之外NADPH有另一來源,
在肝臟和脂肪細胞中由malic enzyme而來。
Acetyl CoA carboxylase: (requires biotin, ATP, and CO2),
controlled activation by insulin, activation by citrate, inhibit by long chain fatty acyl CoA.
The rate limiting enzyme of fatty acid biosynthesis.
Fatty acid synthase(or palmitate synthase):
because palmitate is the only fatty acid that humans can synthesize de novo.
This enzyme is a large, multienzyme complex in the cytoplasm that is
rapidly induced in the liver after a meal by high carbohydrate and rising in insulin levels.
It contains an acyl carrier protein(ACP) requires the vitamin pantothenic acid(Vitmin B5).
Malonyl CoA is the substrate used by fatty acid synthase,
only the carbon of acetyl CoA portion are actually incorporated into the fatty acid produced.
Therefore fatty acid is derived entirely from acetyl CoA.
NADPH is required to reduce the acetyl group added to the fatty acid.
Eight acetyl CoA groups are required to produce palmitate(16:0)
Fatty acyl CoA may be elongated and desaturated using enzyme associated with the SER.
Cytochrome b5 is involved in the desaturation reaction.
These enzyme can’t introduce double bonds past position 9 in the fatty acid.
必須攝取必需脂肪酸的原因!!
Triglyceride(Triacylglycerol synthesis):
TG formation from fatty acids and glycerol 3-phosphate
occurs primarily in liver and adipose tissue.

Liver sends TG to adipose tissue packaged as VLDL.
A small amount amount of TG may be stored in the liver.
Accumulation of significant TG in tissue other than adipose tissue usually indicate pathologic state.
有在其他組織看到有TG的囤積通常是代表病理的現象。
Sources of glycerol 3-phosphate for synthesis of TG:
Two sources of G3P for triglyceride synthesis:
1. Reduction of DHAP from glycolysis by glycerol 3-P dehydrogenase,
an enzyme in both adipose tissue and liver
2. Phosphorylation of free glycerol by glycerol kinase,
an enzyme found in the liver but not in adipose tissue
Glycerol kinase allows liver to recycle the glycerol release
during VLDL metabolism(insulin) back into new TG synthsis.
During fasting(glucagon), same enzyme allows the liver to trap glycerol release into the blood
from lipolysis in adipose for subsequent conversion to glucose.
Adipose lacks glycerol kinase and is strictly depent on glucose uptake to produce DHAP for TG synthesis.
In adipose tissue, GLUT4 transporter is stimulated by insulin, ensuring a good supply of DHAP for TG synthesis.
總結:TG主要可以在肝臟和脂肪細胞中產生,而通常只會在脂肪細胞中儲存,而在肝臟中比較常以VLDL的形態釋放出去給週邊組織分解利用,另外就是脂質和肝臟合成TG的過程有些不同,脂質多了一個kinase所以可以利用甘油來合成,而脂肪細胞只能由糖解作用而來。要特別注意!!
今天簡介到這邊,下次介紹膽固醇的合成和各種 lipoprotein的差異!


 留言列表
留言列表


